Weather forecasting has been an essential aspect of human life for centuries. From agriculture to aviation, accurate weather predictions play a vital role in decision-making processes. With the advancement of technology and access to vast amounts of data, meteorologists have been able to make more accurate predictions. However, even with sophisticated tools and techniques, there is still room for improvement. This is where prediction stations come into the picture. These stations are equipped with state-of-the-art instruments and algorithms that can provide precise and localized weather forecasts. In this article, we will explore the world of prediction stations and how they are revolutionizing weather forecasting.
What is a Prediction Station?

A prediction station, also known as a weather station or meteorological station, is an automated system that collects weather-related data from its surroundings. It consists of various sensors and instruments that measure different variables such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed, and direction. The data collected by these instruments is then transmitted to a central processing unit, where it is analyzed and used to generate weather forecasts.
Weather stations can be found in different forms, including ground-based stations, ship-based stations, and satellite-based stations. Each type has its advantages and limitations, but together they provide a comprehensive view of the weather patterns and conditions.
Components of a Prediction Station
- Sensors – These are the primary components of a prediction station. They are responsible for measuring different weather variables such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed, and direction.
- Data Logger – A data logger is a device that collects and stores the data from the sensors. It can store large amounts of data and transmit it to the central processing unit for analysis.
- Transmitter – The transmitter is responsible for sending the data collected by the sensors to the central processing unit. It can use different methods such as radio waves, satellites, or cellular networks.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU) – This is the brain of the prediction station. It receives data from the sensors and uses algorithms to analyze it and generate weather forecasts.
- Power Supply – A reliable power supply is crucial for a prediction station to function correctly. Most stations use solar panels to generate electricity, but some also have backup batteries.
Types of Prediction Stations
As mentioned earlier, there are different types of prediction stations, each with its unique characteristics and capabilities. Let’s take a closer look at these types and how they contribute to weather forecasting.
Ground-Based Stations
Ground-based stations are the most common type of prediction station. They can be found in various locations such as airports, farms, schools, and private homes. These stations are equipped with multiple sensors that measure different weather variables and transmit the data to a central processing unit.
The advantage of ground-based stations is that they provide detailed information about localized weather conditions. This is especially useful for activities such as farming, where accurate predictions for a specific location are crucial. However, ground-based stations have limitations when it comes to predicting weather patterns on a larger scale.
Ship-Based Stations
Ship-based stations, also known as marine weather stations, are essential for maritime operations. Since ships can travel to remote areas where ground-based stations are not available, these stations play a vital role in providing weather information for those regions. Ship-based stations are equipped with specialized sensors that can withstand harsh marine conditions such as saltwater corrosion and high wind speeds.
One of the primary advantages of ship-based stations is their ability to collect data from different parts of the ocean, providing a more comprehensive view of weather patterns and conditions. However, these stations are limited to sea areas and cannot provide accurate predictions for land-based locations.
Satellite-Based Stations
Satellite-based stations use remote sensing technology to collect weather data from space. These stations are equipped with advanced sensors that can measure various weather variables from a distance. The data collected by these stations is then transmitted to the ground stations for analysis.
Satellite-based stations have the advantage of providing global coverage, making them essential for predicting weather patterns on a larger scale. They are particularly useful for monitoring weather conditions in remote and inaccessible areas. However, their effectiveness may be hindered by factors such as cloud cover and atmospheric interference.
How Prediction Stations Help Improve Weather Forecasting

Weather forecasting is a complex process that requires vast amounts of data to provide accurate predictions. In the past, meteorologists had to rely on limited data collected from ground-based stations, which often resulted in inaccurate forecasts. However, with the advent of prediction stations, this has changed significantly. Here’s how prediction stations help improve weather forecasting:
1. Real-Time Data Collection
Prediction stations collect real-time data from their surroundings, providing meteorologists with up-to-date information about current weather conditions. This is particularly useful during severe weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods, where every minute counts. With real-time data, meteorologists can issue timely warnings and take necessary precautions to minimize the potential impact of these events.
2. More Accurate Predictions
By collecting data from different locations, prediction stations provide a more comprehensive view of weather patterns and conditions. This allows meteorologists to make more accurate predictions for specific regions or even the entire globe. With the help of sophisticated algorithms, prediction stations can analyze vast amounts of data and generate precise forecasts that were not possible before.
3. Localized Weather Forecasts
Ground-based prediction stations play a crucial role in providing localized weather forecasts. By collecting data from a specific location, these stations can provide accurate predictions tailored to that area. This is particularly useful for activities such as farming, where the weather conditions in a particular region can differ from those in the neighboring areas.
4. Continuous Monitoring
Prediction stations operate 24/7, providing continuous monitoring of weather conditions. This is especially useful for tracking the development of severe weather events such as hurricanes and tornadoes. With real-time data, meteorologists can track the movement and intensity of these events and issue timely warnings to the public.
5. Improving Climate Research
Prediction stations not only help with short-term weather forecasting but also play a vital role in long-term climate research. By collecting data over extended periods, these stations contribute to climate modeling and help scientists understand how our planet’s climate is changing over time. This information is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change.
The Future of Prediction Stations

As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more powerful and sophisticated prediction stations in the future. Some of the developments that we may witness include:
1. More Accurate Sensors
The accuracy of a prediction station depends on the quality of its sensors. In the future, we can expect to see more advanced sensors that can measure additional variables and provide even more accurate data. These sensors may also be able to withstand harsh weather conditions, making them suitable for use in extreme environments.
2. Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence has already made its way into various fields, and weather forecasting is no exception. In the future, we can expect to see an increased use of AI in prediction stations, making them more efficient at analyzing vast amounts of data and generating more accurate predictions.
3. Integration with Smart Devices
With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), we can expect to see prediction stations integrated with smart devices such as smartphones, tablets, and smart home systems. This will allow individuals to access real-time weather information from anywhere, making it easier to plan their activities accordingly.
Challenges Faced by Prediction Stations
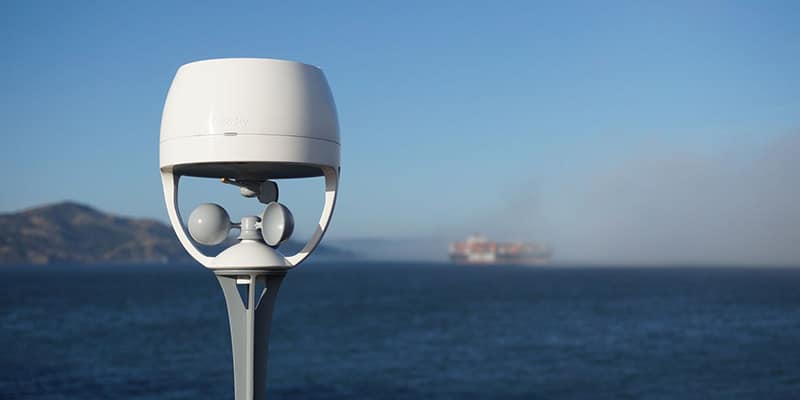

While prediction stations have revolutionized weather forecasting, they still face some challenges that need to be addressed. Some of these challenges include:
1. High Cost
Setting up a prediction station requires significant investments in terms of equipment, maintenance, and personnel. This can be a challenge for countries with limited resources, making it difficult for them to establish a reliable network of prediction stations.
2. Maintaining Accuracy
As accurate as prediction stations may be, they are not infallible. Weather conditions can change rapidly, and if the sensors or data loggers are faulty, it can lead to inaccurate forecasts. It is crucial to ensure proper maintenance and calibration of these stations to maintain their accuracy.
3. Limited Coverage in Remote Areas
While satellite-based stations provide global coverage, ground-based stations are limited to accessible areas. This makes it difficult to obtain accurate predictions for remote and inaccessible regions, which are often prone to severe weather events.
Conclusion
Prediction stations have come a long way since their inception, and they continue to play a vital role in weather forecasting. With advancements in technology, we can expect to see more accurate and efficient prediction stations in the future. These stations will not only help improve short-term weather forecasts, but also contribute to long-term climate research. As our planet’s climate continues to change, the importance of prediction stations in providing timely and accurate weather information cannot be overstated. They are truly revolutionizing weather forecasting and helping us make more informed decisions to protect ourselves and our environment.